Ask the Expert: Why is wavelength important in laser hair removal?
BY SAMANTHA WELCH, ESTHETICIAN
As a laser technician, I cannot stress enough the significance of using the right specifications when it comes to at-home laser hair removal.
The success of your treatments and the safety of your skin relies on several key factors.
Wavelength is important for several reasons:
- Effectiveness – Your IPL or laser device's wavelength plays a crucial role in determining how effectively it targets the melanin within your hair follicles. When your device operates at an appropriate wavelength, the laser energy is optimally absorbed by the melanin, resulting in the destruction of the hair follicle and preventing hair regrowth.
- Safety – Different wavelengths have varying abilities to penetrate the skin and absorb melanin. Choosing the right wavelength for your skin and hair type minimizes the risk of side effects, such as skin irritation, burns, or changes in skin pigmentation.
- Skin and hair type compatibility – Each wavelength is more or less suitable for specific skin and hair types. For example, some shorter wavelengths work best for lighter skin tones and finer hair, while longer wavelengths are more effective for darker skin tones and coarser hair. Selecting the appropriate wavelength for your skin and hair type ensures optimal results and reduces the risk of complications.
The repercussions of using a home device with incompatible settings for your skin and hair type includes: ineffective hair removal, skin irritation, burns, and even permanent pigmentation issues.
These are just a few of the potential risks, not mentioning all the effort, money, and time wasted from using the wrong IPL device.
We understand that choosing the right at-home laser hair removal device can be a daunting task, so we’re here to guide you through the process.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the basics of laser hair removal, explain wavelength in detail, and help you understand how to choose the right device for your skin and hair type.
By the end, you will hopefully be equipped with the necessary information to choose an IPL or laser device that is both safe and effective for your personal use.
- Ask the Expert: Why is wavelength important in laser hair removal?
- Cheat Sheet: At-Home Laser Hair Removal Devices Comparison Chart
- What Is Wavelength?
- Laser & IPL in Light-Based Therapies
- How Laser Hair Removal Works
- IPL vs. Laser
- Why Wavelength Matters in Laser Hair Removal & How It Affects Treatment
- Matching Wavelength to Skin Tone & Hair Color
- Laser/IPL Types & Depth of Penetration
- Use Cases
- Understanding Your Skin & Hair Type
- Safety & Efficacy
- References:
Cheat Sheet: At-Home Laser Hair Removal Devices Comparison Chart
Esthetician Tip: Save time by process of elimination. Compare by skin tone coverage, technology, power, safety (cooling), and other features.

| wdt_ID | Image | Device/Brand | Product | Max Energy Fluence | Wavelength | Skin Tone Coverage | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | Cooling/Pain-free |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
https://healthybeautiful.com/review/viqure-depimini-808nm-diode-laser-machine-in-depth-esthetician/ | ViQure EpiPro | 20.0 | 808nm | I-VI | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Advanced TEC (Thermoelectric Cooling) + Wind Cooling (0°C~5°C) + Cooling gel (sold separately) |
| 2 |  |
https://healthybeautiful.com/JOVS-X-3-in-1-IPL | JOVS X™ 3-in-1 IPL (OPT) | 7.0 | 590~1200nm | I-V | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Sapphire Cooling System | |
| 3 |  |
https://healthybeautiful.com/review/ulike-sapphire-air3-an-in-depth-review-by-estheticians/ | Ulike Sapphire Air3 | 6.3 | 560~1200nm | I-IV | Y | Y | Y | Y | Contact epidermal temperature of treatment area around 10-20°C (50-68°F) | ||
| 4 |  |
https://healthybeautiful.com/NAISIGOO-The-Shiner | NAISIGOO The Shiner | 4.0 | 550~1200nm | I-V | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 60℉ | |
| 5 |  |
https://healthybeautiful.com/Bosidin-Pioneer-Pro-Official | BoSidin Pioneer-Pro (OPT) | 6.0 | 650~910nm | I-V | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Dynamic Cooling Device (DCD) |
What Is Wavelength?
Wavelength is a crucial aspect of laser light as it dictates how the light interacts with matter.
It influences the color of the light and its ability to penetrate different materials, which is essential for various applications.
Measuring Wavelength
Wavelength is typically measured in nanometers (nm), with one nanometer equal to one billionth of a meter.
Different types of lasers emit light at specific wavelengths, which are chosen based on the intended application.
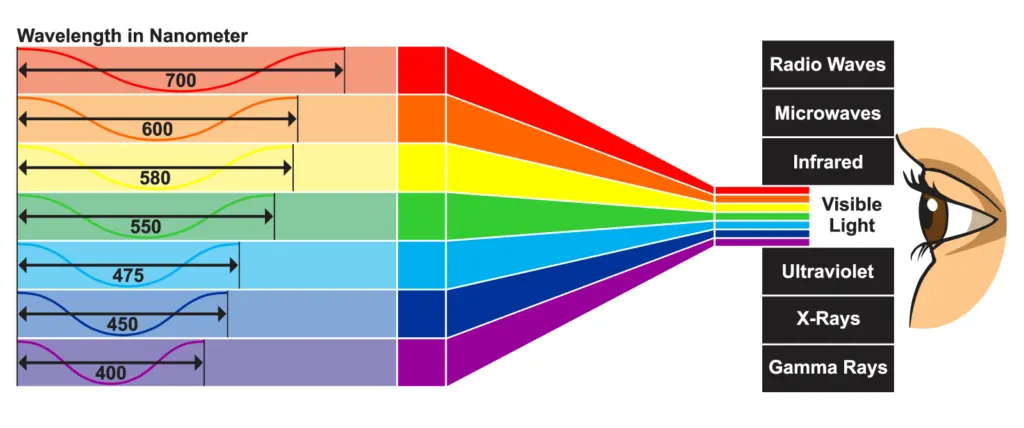
Relationship to Color
Lasers emitting light within the visible spectrum can produce a range of colors depending on their specific wavelength.
The human eye perceives different wavelengths of light as different colors.
For example, shorter wavelengths appear blue or violet, while longer wavelengths appear red or orange.
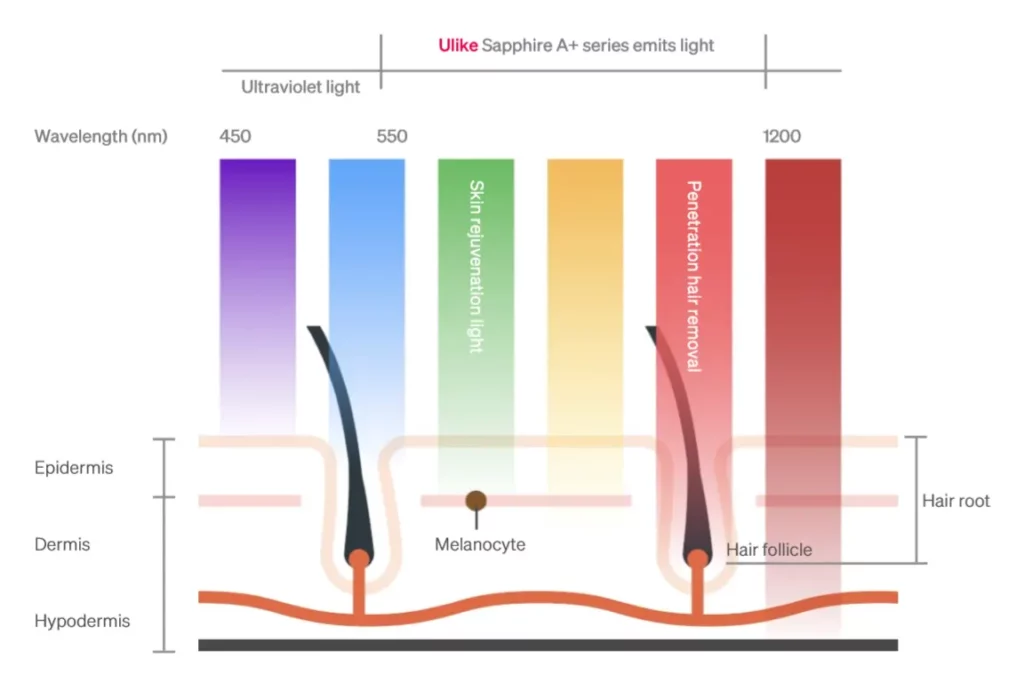
Just as visible light consists of a spectrum of colors, laser devices operate within a broader range that includes invisible wavelengths, such as infrared and ultraviolet.
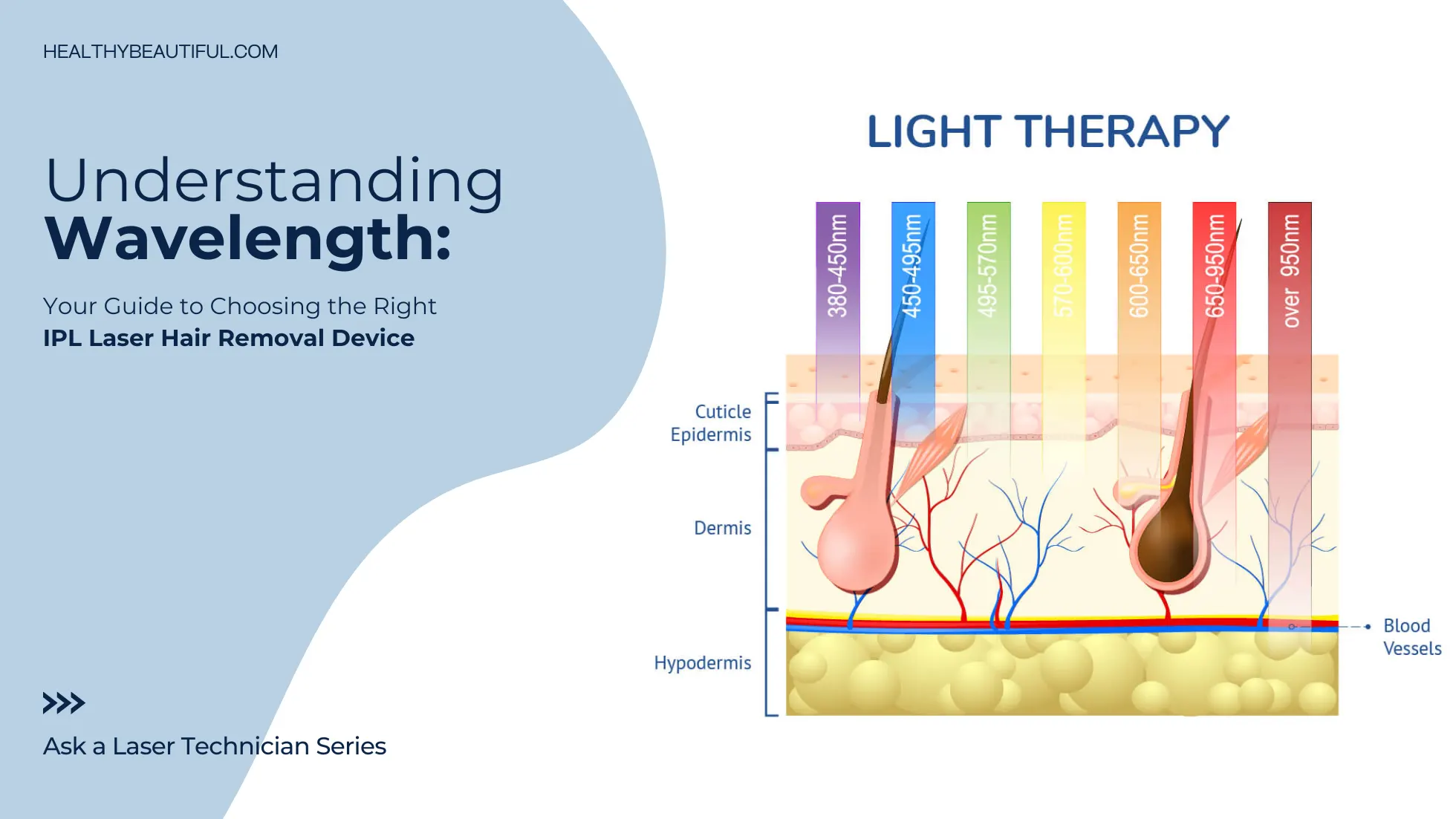
Laser & IPL in Light-Based Therapies
Light-based therapies harness specific wavelengths to address a myriad of skincare concerns including laser hair removal, skin rejuvenation, and phototherapy.
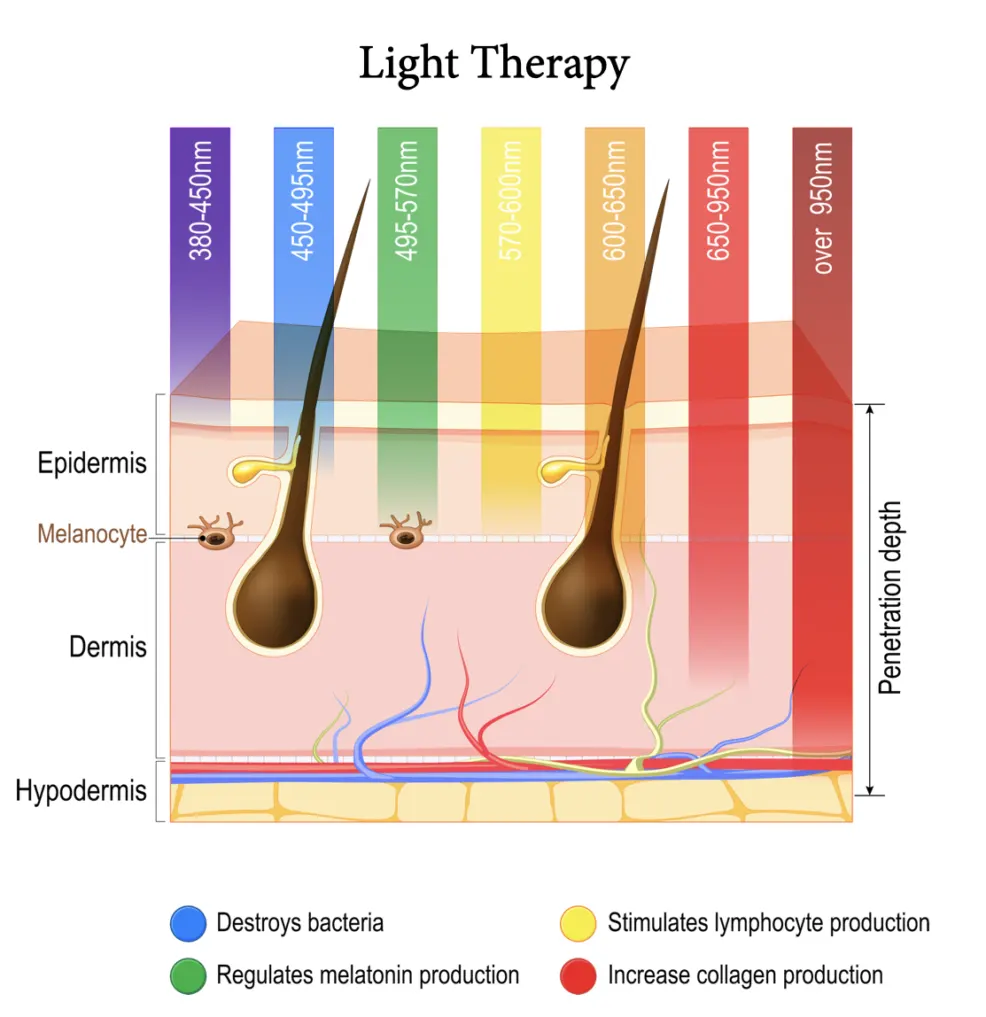
The primary goal is to select a wavelength that effectively interacts with the target chromophore (such as melanin, hemoglobin, or water) in the skin while minimizing potential damage to surrounding tissues.
Use Cases:
- Acne Treatment – Blue light (400-470 nm) targets acne-causing bacteria; Red light (620-700 nm) reduces inflammation and promotes healing.
- Tattoo Removal (532-1064 nm) – Selectively targeting tattoo ink particles for gradual elimination by the body.
- Skin Rejuvenation (500-1200 nm) – Stimulates collagen production, improving skin texture and reducing signs of aging.
- Vascular Lesions (532-1064 nm for laser, 515-1200 nm for IPL): Laser and IPL can be used to treat vascular lesions such as spider veins, broken capillaries, and rosacea. The light energy is absorbed by the blood vessels, causing them to heat up and eventually be reabsorbed by the body.
- Pigmented Lesions (532-1064 nm for laser, 515-1200 nm for IPL): Both technologies can target pigmented lesions such as age spots, freckles, and liver spots. The light energy is absorbed by the melanin in the lesion, causing it to break up and be gradually eliminated by the body.
- Laser Hair Removal (700-1200nm) – Targets melanin in hair follicles for inhibiting hair growth while sparing surrounding tissue.
Different wavelengths have varying abilities to penetrate the skin and absorb melanin, making some wavelengths more suitable for certain skin and hair types than others.
Selecting the right wavelength is crucial for achieving safe, effective, and long-lasting results.
How Laser Hair Removal Works
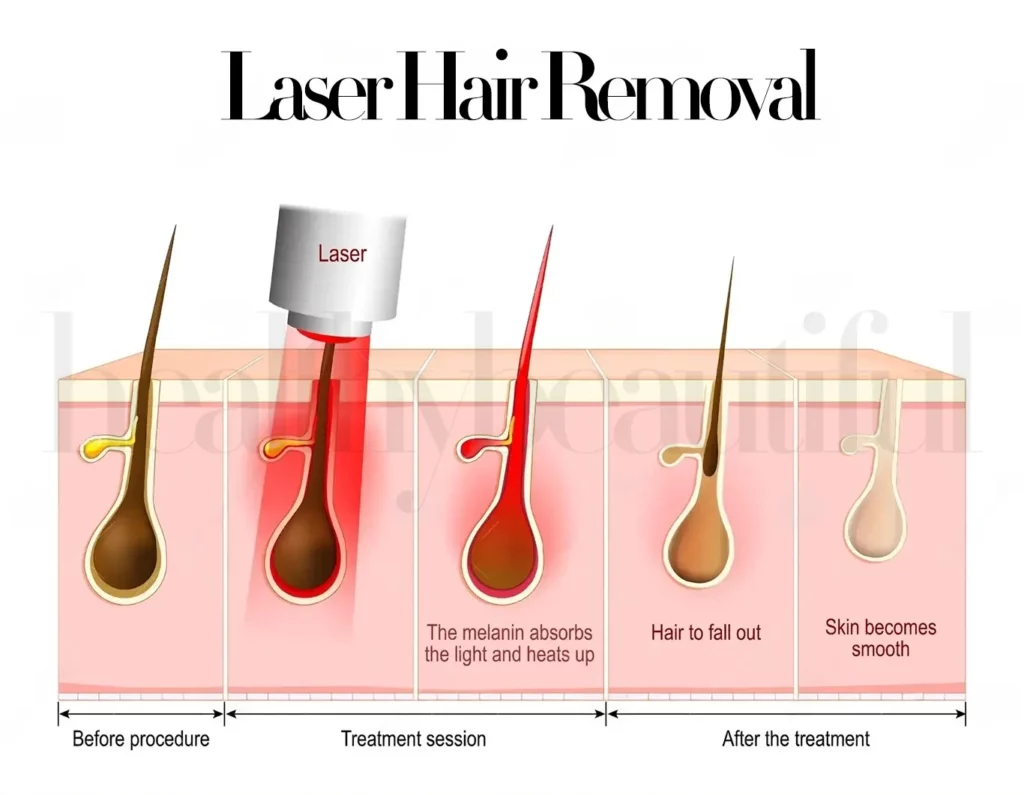
Laser hair removal is a popular and effective method that utilizes concentrated light energy to target and remove unwanted hair.
The process works by targeting the melanin pigment present in the hair follicle with specific wavelengths of light energy.
During the treatment, the laser light is directed at the desired area, and the melanin in the hair follicle absorbs the light energy.
This concentrated energy then converts into heat, causing damage to the hair follicle and inhibiting future hair growth.
But not all lasers are created equal. Different hair colors and skin tones require specific laser wavelengths for optimal results.
This is because the melanin content varies among individuals, and the wavelength must be precisely matched to target the melanin in the hair while minimizing potential harm to the surrounding skin tissue.
This is where the role of wavelength comes into play.
IPL vs. Laser
While both laser and IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) devices are commonly used for hair removal, they differ in their approach to wavelength emission and targeting melanin in the hair follicles.
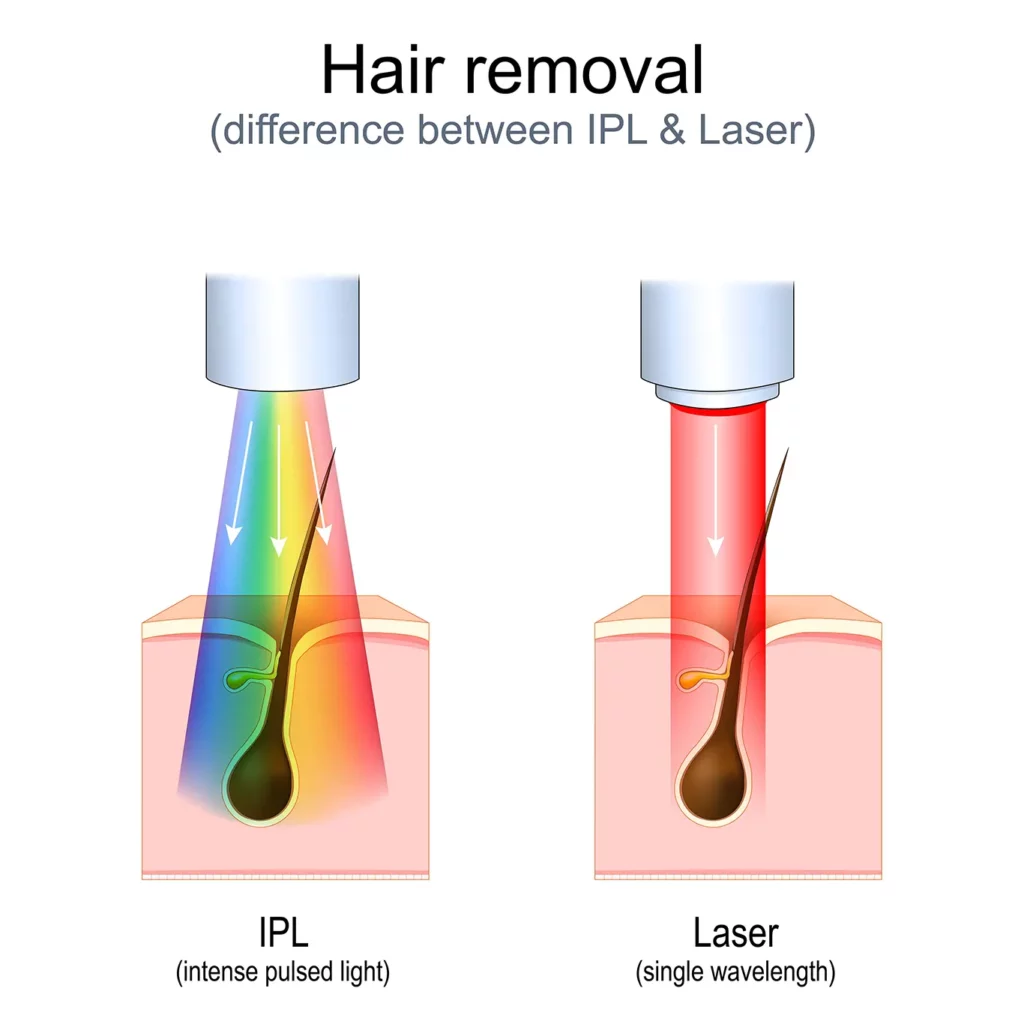
| Aspect | Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) | Laser Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Monochromaticity | Emits a broad spectrum of light. | Emits a single, precise wavelength of light. |
| Wavelength Precision | Offers a broader range of wavelengths. | Can be fine-tuned to emit specific wavelengths. |
| Depth of Penetration | Variable depth penetration depending on filters. | Penetrates to specific depths within the skin. |
| Selective Absorption | Less selective absorption due to broad spectrum. | Highly selective absorption based on wavelength chosen. |
| Examples | 500-600 nm for pigmentation, 800-1200 nm for hair removal. | 532 nm for vascular lesions, 1064 nm for hair removal. |
Why Wavelength Matters in Laser Hair Removal & How It Affects Treatment
Wavelength is crucial for both the effectiveness and safety of hair removal procedures.
It determines the depth of light penetration into the skin and how effectively the laser energy is absorbed by the melanin in the hair follicles.
The optimal wavelength allows precise targeting of hair follicles while minimizing absorption by surrounding skin tissue.
An inappropriate wavelength can lead to ineffective hair removal or cause skin damage by overheating the epidermis or failing to penetrate deep enough.
Matching the right wavelength to your skin and hair type ensures safe and successful permanent hair reduction.
Melanin Absorption
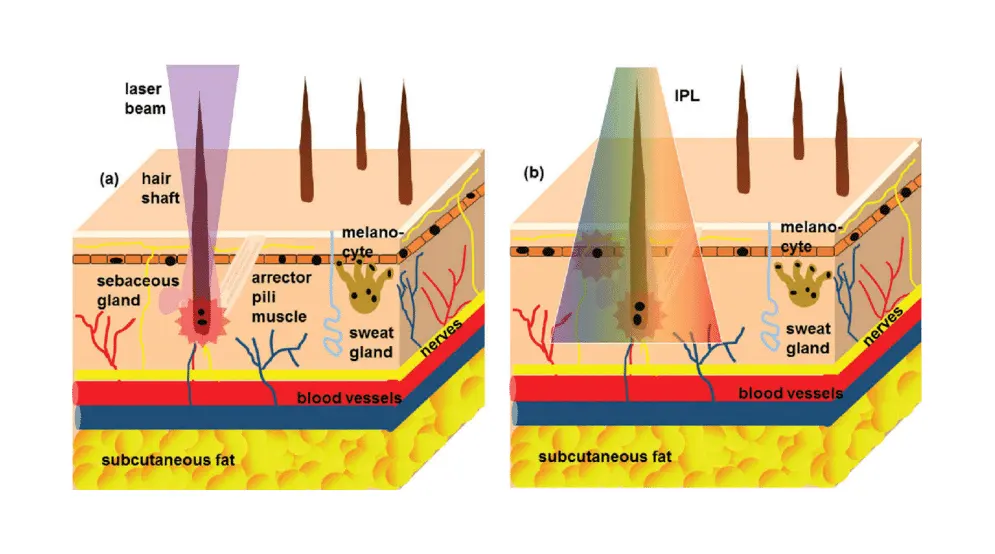
Melanin is the pigment that gives color to hair and skin. It acts as the target chromophore (light-absorbing molecule) in laser hair removal.
The laser energy needs to be absorbed efficiently by the melanin in the hair follicles to generate enough heat to disable the follicles permanently.
Different wavelengths have varying absorption coefficients for melanin. Some wavelengths are better absorbed by melanin than others.
The wavelengths that are highly absorbed by melanin can penetrate deeply enough into the skin to reach and heat up the hair follicles effectively.
For example, the 755nm alexandrite and 810nm diode lasers are well-absorbed by melanin, making them highly effective for laser hair removal on patients with darker skin tones.
In contrast, wavelengths that are poorly absorbed by melanin may not transfer enough energy to the follicles for permanent hair reduction, leading to suboptimal results.
Additionally, wavelengths that are too well-absorbed by epidermal melanin can cause surface burning of the skin.
So an optimal melanin absorption range exists for safe and efficacious laser hair removal.
Therefore, selecting the ideal wavelength that balances melanin absorption in follicles
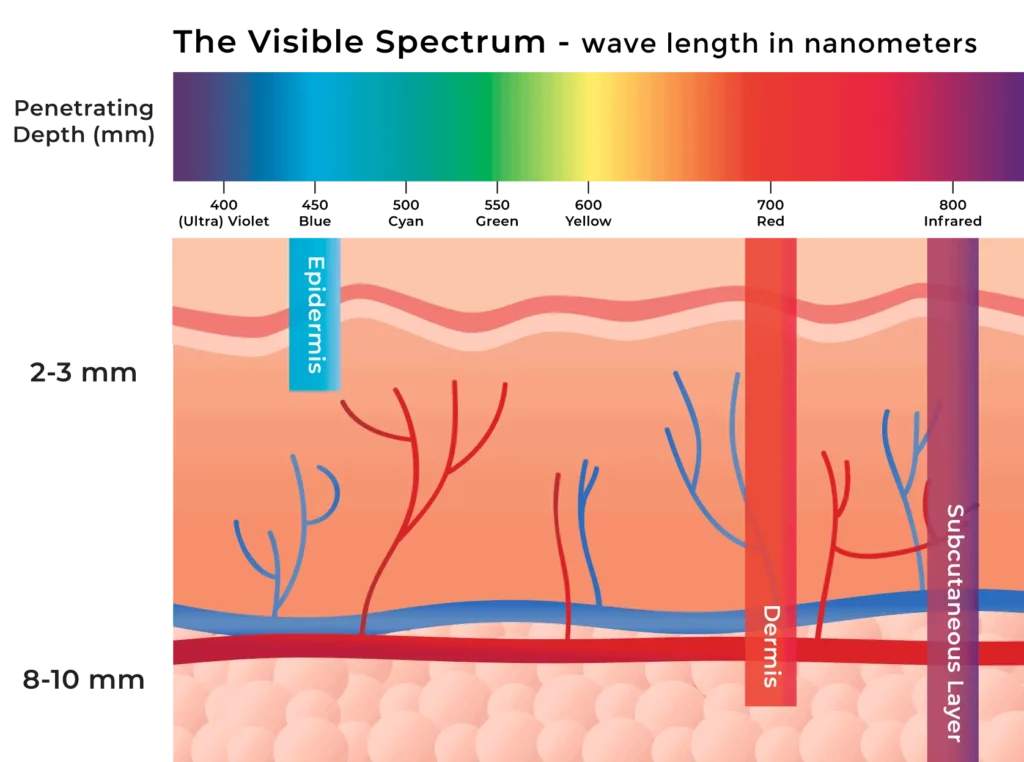
Depth of Penetration

The depth of penetration is another key factor that makes wavelength selection critical for effective and safe laser hair removal.
Laser light penetrates into the skin based on its wavelength and the optical properties of the tissue.
For laser hair removal to be successful, the laser energy needs to penetrate deep enough to reach and sufficiently heat up the entire hair follicle, which can extend several millimeters into the dermis.
Different wavelengths have varying abilities to penetrate the skin's layers.
- Longer wavelengths penetrate deeper, targeting thicker, coarser hair follicles beneath the surface.
- Shorter wavelengths are more suitable for finer, superficial hairs closer to the skin's surface.
Wavelengths that penetrate too superficially may only heat up the hair shaft near the surface, failing to disable the deeper portions of the follicle. This leads to ineffective and temporary hair removal.
On the flip side, wavelengths that penetrate too deeply beyond the hair follicles can potentially cause unwanted heating and damage to surrounding tissues like nerves and blood vessels.
The optimal wavelength strikes a balance – penetrating deep enough to effectively target the entire hair follicle while limiting excessive depth that increases risk of side effects.
Different skin types also affect depth of penetration. So choosing a wavelength that can penetrate appropriately for a patient's skin type is crucial for safe and successful outcomes.
Matching Wavelength to Skin Tone & Hair Color

Skin Type
Different skin tones have varying amounts and distribution of melanin pigment.
Lighter skin types have less melanin, while darker skin tones have higher melanin concentrations.
Certain wavelengths may be overly absorbed by excess melanin in darker skin, potentially causing burns or hyperpigmentation.
Other wavelengths may not penetrate deeply enough in highly pigmented skin.
Therefore, the wavelength must be carefully selected to ensure proper heating of follicles without damaging the epidermis based on the patient's skin color.
Hair Type
Hair color is determined by the melanin content within the hair shaft and follicle.
Lasers are most effective on coarser, darker terminal hairs that have high melanin concentration.
Fine, light-colored hairs with low melanin may not absorb the laser energy sufficiently.
As such, a wavelength that is highly absorbed by the melanin present in the patient's hair type must be used for optimal follicle heating and permanent reduction.
Getting this wavelength “match” right is the key to achieving effective, permanent hair reduction while preventing complications across different skin and hair types.
Let's take a look at some of the most common wavelengths used in laser hair removal devices and how they correspond to different skin and hair combinations.
Laser/IPL Types & Depth of Penetration
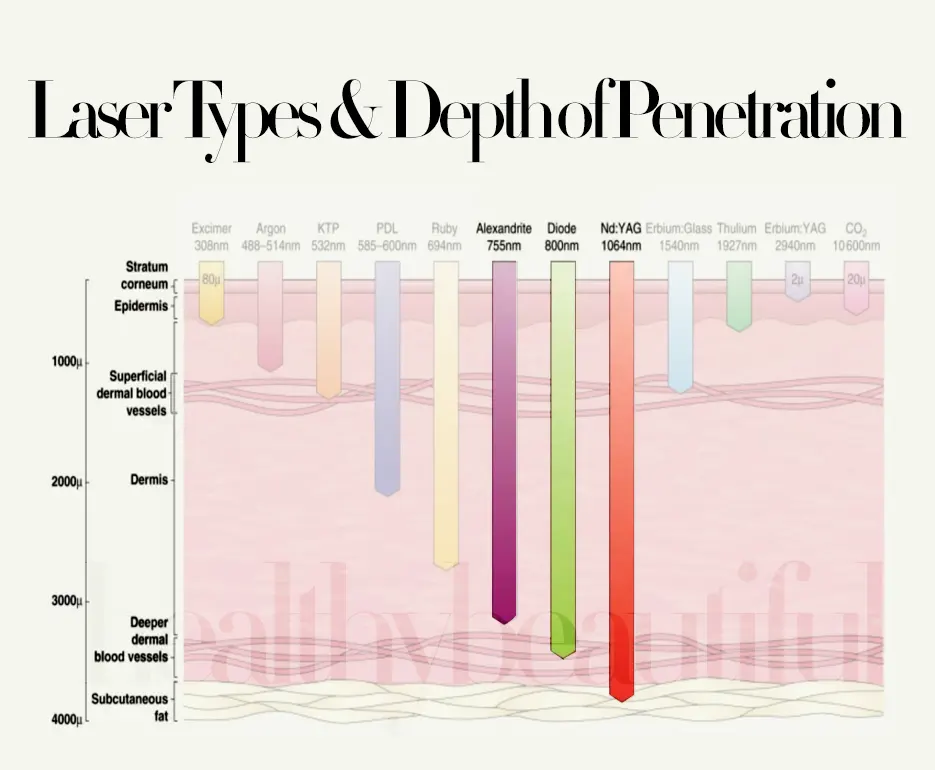
Laser & IPL Compatibity: Skin & Hair
| Treatment Type | Wavelength (nm) | Target Chromophore | Skin & Hair Type Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser (Alexandrite) | 755nm | Melanin | Lighter skin tones, finer hair |
| Laser (Diode) | 810nm | Melanin | Wide range of skin and hair types |
| Laser (Nd) | 1064nm | Melanin | Darker skin tones, coarser hair |
| IPL | 500-1200nm (broad spectrum) | Melanin, Hemoglobin | Various skin types, multiple treatments |
755nm Alexandrite
- Ideal for lighter skin tones (Fitzpatrick I-III) and finer hair
- The shorter wavelength targets the lower melanin levels in lighter hair effectively
- Minimizes the risk of skin irritation or burns on fair skin
- Not as suitable for darker skin tones due to the increased risk of skin damage.
- Not available for home use, and treatments are usually performed by professionals in a clinical setting
Popular At-Home Laser Hair Removal using Alexandrite Laser: NONE.
800+nm Diode
- Highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of skin tones and hair colors
- Its wavelength provides a balance between melanin absorption and depth of penetration, making it suitable for targeting both finer and coarser hairs.
- Some devices using this wavelength are available for home use, but professional treatments may still yield better results.
Popular At-Home Laser Hair Removal using Diode Laser: ViQure EpiPro, Tria 4x
1064nm Nd:YAG
- Optimal for individuals with darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick IV-VI) and coarser, thicker hair
- The longer wavelength penetrates deeper into the skin, targeting higher melanin levels
- Reduces the risk of skin damage on darker complexions
- Not available for home use, and treatments are usually performed by professionals in a clinical setting
Popular At-Home Laser Hair Removal using Nd:YAG Laser: NONE.
IPL – Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
- For lighter skin tones (Fitzpatrick I-III) and finer hair, a lower wavelength range of 500-700nm is generally recommended.
- For medium to olive skin tones (Fitzpatrick III-V) and medium to dark hair, a broader wavelength range of 600-900nm may be more suitable.
- For darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick V-VI) and coarser, thicker hair, a higher wavelength range of 700-1200nm is often advised.
Some IPLs have a unique feature that allows you to adjust the wavelength range to suit your skin and hair type in different areas of the body.
Examples of this are: JOVS X™ 3-in-1 IPL (OPT), BoSidin Pioneer-Pro (OPT) / JOVS Venus Pro (OPT)
IPL devices are the most common type found in at-home hair removal devices.
They are generally more affordable and accessible for home use, but they may require more treatment sessions and may not be as effective for darker skin tones or coarser hair.
They may also not provide the same level of precision and results as laser treatments.
Popular At-Home Laser Hair Removal using IPL: Ulike Sapphire Air3, NAISIGOO The Shiner, Beam Home IPL, Braun Silk-Expert Pro 5, etc.
Use Cases
Use Case: Professional & At-Home Lasers (Diode, Alexandrite, nd:YAG)
Here's an example to explain the importance of choosing the correct wavelength for effective and safe laser hair removal.
Let's say you have fair skin with light brown hair.
In this case, an ideal wavelength for your skin and hair type would be around 755nm, which is emitted by an Alexandrite laser.
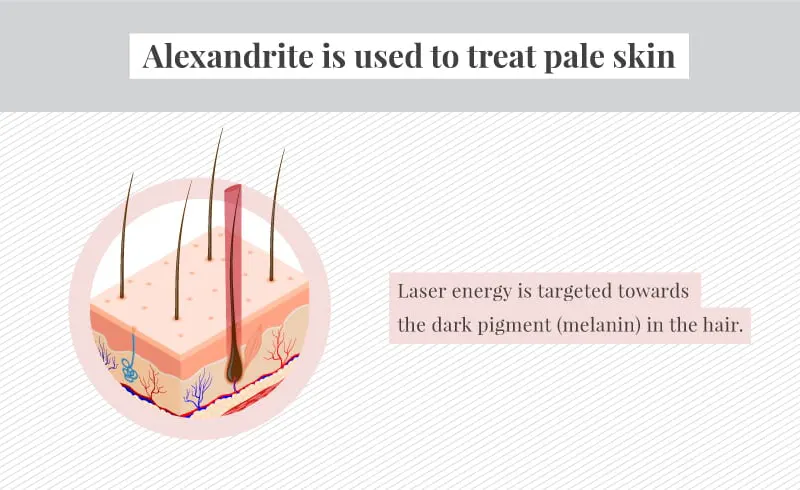
If you choose a device with the correct 755nm wavelength:
- The laser light will be effectively absorbed by the melanin in your light brown hair follicles
- It will generate enough heat to disable the follicles and prevent future hair growth
- At the same time, this wavelength is safe for fair skin as it doesn't penetrate too deeply
However, if you unknowingly choose a device with a longer wavelength, say 1064nm (Nd:YAG laser):
- This wavelength is better suited for darker skin tones and coarser hair
- It may not be absorbed as well by the melanin in your light brown hair
- As a result, the treatment would be less effective in disabling your hair follicles
- Additionally, the deeper penetration could potentially cause skin irritation or burns on your fair skin
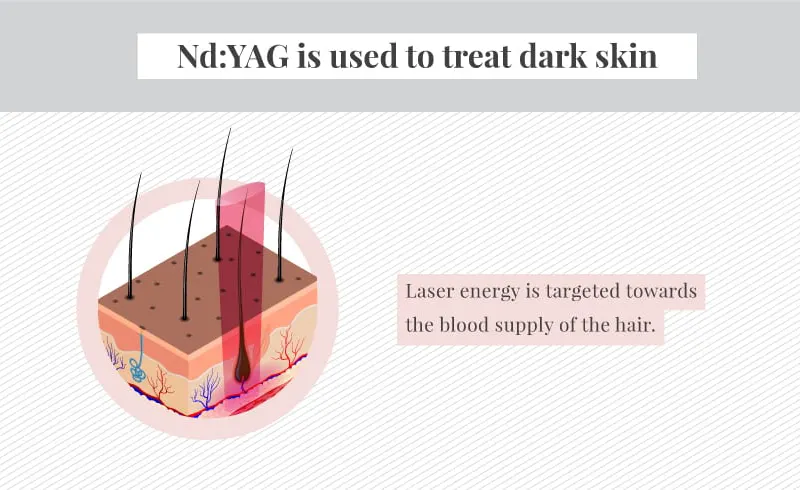
Conversely, if you have olive skin with dark, coarse hair and use a shorter 755nm wavelength device:
- The shorter wavelength may not penetrate deeply enough to reach your thicker hair follicles
- This would lead to suboptimal results and incomplete hair removal
- There's also a risk of the laser energy being absorbed by the increased melanin in your olive skin, causing potential burns or pigmentation issues.
This example highlights how choosing the wrong wavelength, either too long or too short for your specific skin and hair type, can compromise the treatment's effectiveness and safety.
Use Case: At-Home IPL Devices
With IPL hair removal devices, the wavelength range is broader compared to laser devices that use a single specific wavelength.
Most at-home IPL devices emit light in the 500-1200nm wavelength range.
If you have fair skin and light hair, an ideal wavelength range would be around 500-700nm:
- Choosing an IPL device that emits light in this lower wavelength range ensures the light energy is effectively absorbed by the melanin in your light hair follicles
- At the same time, the shorter wavelengths don't penetrate too deeply into your fair skin, reducing risk of burns or irritation
However, if you used an IPL device with a wavelength range of, say, 800-1200nm:
- These longer wavelengths may not be well-absorbed by the melanin in your light hair follicles
- This would make the treatment less effective for disabling the follicles and preventing hair growth
- There's also a risk of the longer wavelengths penetrating too deeply into your fair skin, potentially causing damage
On the other hand, if you have darker skin and use an IPL device with only shorter 500-700nm wavelengths:
- The shorter wavelengths may get overly absorbed by the increased melanin in your darker skin tone
- This increases the risk of burns, pigmentation issues, or other skin damage
- The shorter wavelengths may not reach the deeper hair follicles in coarser, thicker hair
So with at-home IPL devices, it's crucial to match your skin and hair type to the optimal wavelength range offered by the device for safe and effective hair removal.
All that said, these are usually cited in your devices’ user manual through a skin tone and hair color chart.
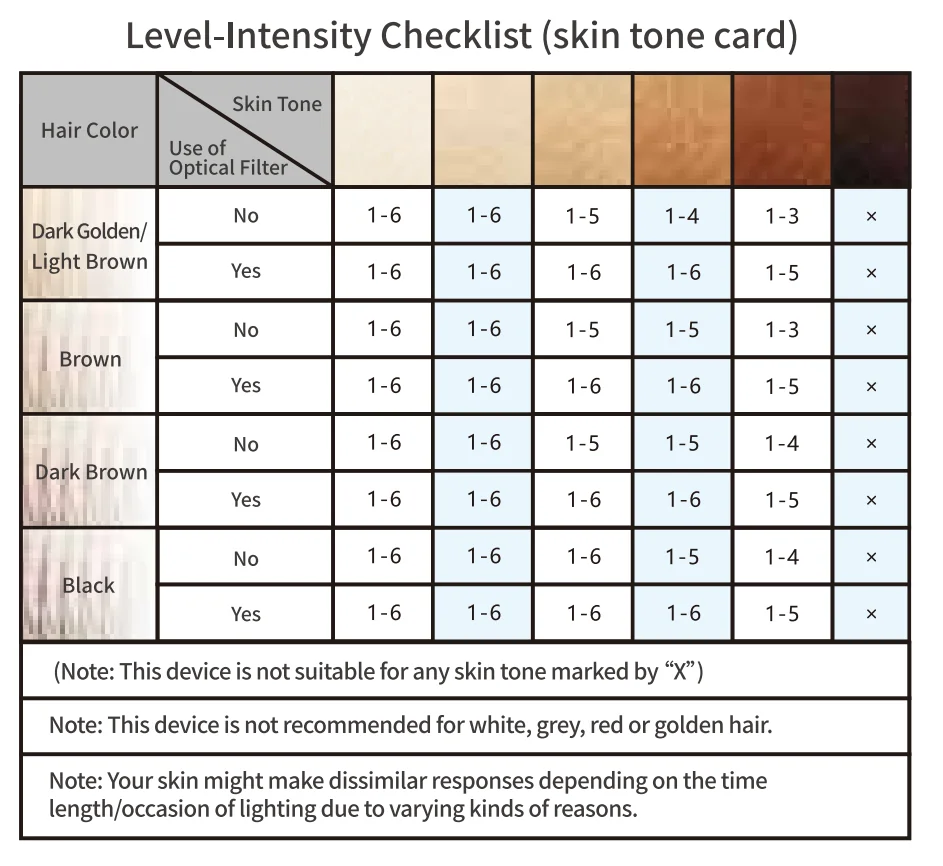
Most reputable at-home laser hair removal and IPL device manufacturers provide detailed information about the wavelength specifications in the user manual for their products.
Marketing materials will also often include a chart or table mapping different skin tones and hair colors covered by their laser devices.
Make sure to check before buying to save you from accidentally choosing a device with an incompatible wavelength that could lead to ineffective hair removal or potential skin irritation.
By ensuring you understand and match the wavelength specifications to your specific skin and hair characteristics, you can make an informed decision and increase the chances of achieving safe, long-lasting results with your at-home laser or IPL hair removal device.
Understanding Your Skin & Hair Type

The Fitzpatrick Skin Type Classification
The Fitzpatrick skin type classification is a widely recognized system that categorizes skin types based on their reaction to sun exposure and their melanin content.
It ranges from Type I (pale white skin that always burns and never tans) to Type VI (deeply pigmented dark brown to black skin that never burns).
Knowing your Fitzpatrick skin type is crucial when choosing a laser hair removal device, as different skin types require different wavelengths for safe and effective treatment.
To determine your skin type, you can refer to the Fitzpatrick skin type classification and assess your skin's reaction to sun exposure.
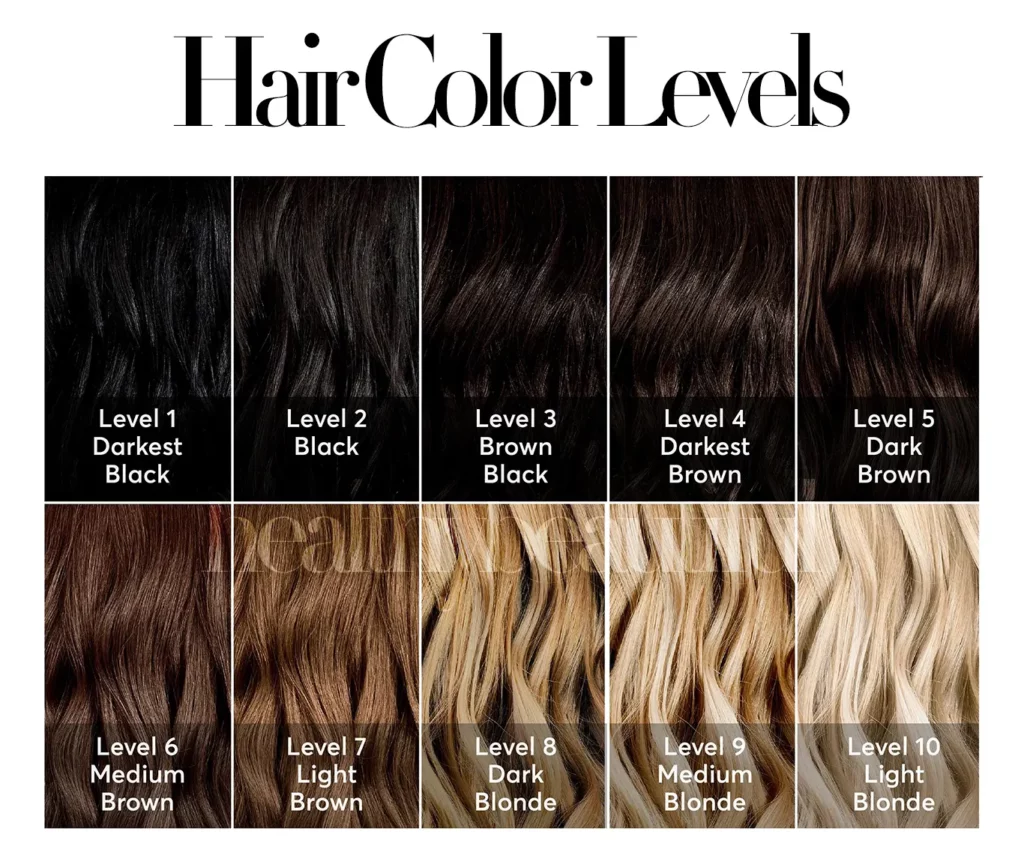

How to Identify Your Hair Color
Here are some tips on how to determine your hair color accurately when choosing a laser hair removal device:
- Categorize your natural hair color – Take a close look at the hair growing from your head, arms, legs, or any other area you plan to treat. Examine the hair in natural, bright lighting conditions. Identify the predominant shade – is it light blond, red, brown, dark brown/black?
Generally, hair colors are categorized into the following groups: black, dark brown, brown, light brown, blonde, red, gray, and white. Determine which category best represents your natural hair color. - Untreated hair – For the most accurate assessment, examine hair that has not been dyed, highlighted, or chemically treated. Hair coloring and processing can alter the natural pigmentation, affecting laser hair removal.
- Multiple shades – If you notice your hair has multiple shades or highlights, focus on the darkest, most prominent color. Laser devices target melanin, so the darkest pigment will require the most appropriate wavelength.
- Coarseness/thickness – In addition to color, take note of the coarseness and thickness of your hair. Coarser, thicker hair may require a longer wavelength to penetrate deeper into the follicle.
- Refer to manufacturer guidelines – Most at-home laser hair removal devices provide detailed guidelines on matching hair colors to the appropriate wavelength settings or models. Refer to these resources for accurate recommendations based on your hair type.
To choose the best laser hair removal device, you need to know your hair color, thickness, coarseness, and skin tone.
This helps you find a device that targets the melanin in your hair effectively, while also reducing the chance of skin irritation or damage.
Keep in mind that laser hair removal is typically most effective on darker, coarser hair and less effective on lighter, finer hair.
If you're unsure about your hair color or need further guidance, consult with a professional or contact the device manufacturer for assistance.
Safety & Efficacy
The Risks of Choosing the Wrong Wavelength
While laser hair removal is generally safe and effective when performed properly, choosing the wrong wavelength for your skin and hair type can have significant risks and potential side effects.
It's crucial to understand these risks to prioritize your safety and achieve optimal results.
- Ineffective Treatment – If the wavelength you select is not well-absorbed by the melanin in your hair follicles, the laser energy may not be effectively converted into heat, rendering the treatment ineffective. This can lead to incomplete hair removal, with hairs remaining or regrowing quickly after the treatment. Essentially, you may not see the desired long-lasting results, despite investing time and money into the process.
- Skin Irritation and Burns – Perhaps the most concerning risk of using the wrong wavelength is the potential for skin damage. If the wavelength is too long or too short for your skin tone, the laser energy may be overly absorbed by the melanin in your skin, rather than your hair follicles. This can cause various issues, including:
- Skin irritation and redness
- Painful burns or blisters
- Hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin)
- Hypopigmentation (lightening of the skin)
- Scarring or permanent skin discoloration
These side effects can be not only painful but also potentially disfiguring, affecting your appearance and self-confidence.
The Importance of Safety and Effectiveness
Laser hair removal is a cosmetic treatment, and as such, safety and effectiveness should be the top priorities.
Choosing the wrong wavelength not only compromises the results but also puts your skin at risk of harm.
It's essential to prioritize your well-being and ensure that the device you choose is tailored to your specific needs.
By carefully reviewing the manufacturer's guidelines, and selecting the appropriate wavelength for your skin and hair type, you can minimize the risks and maximize the chances of achieving safe, effective, and long-lasting hair removal results.
Remember, your safety and satisfaction should be the primary considerations when choosing a laser hair removal device.
Taking the time to understand the importance of wavelength specifications and making an informed decision can help you avoid potential risks and enjoy a positive, successful hair removal experience.
Safety Precautions
To ensure a safe and effective at-home laser hair removal experience, it's essential to follow these safety precautions:
- Follow all safety instructions – Carefully read and adhere to all safety instructions provided with the device. This includes proper usage, maintenance, and storage guidelines.
- Avoid sensitive areas – Do not use the device on sensitive areas such as the eyes, ears, or genitals, unless the device manual explicitly states it is safe to do so.
- Medical conditions – If you have certain medical conditions, such as skin disorders, a history of skin cancer, or are taking photosensitive medications, consult with a medical professional before using a laser hair removal device.
- Understand and select the appropriate wavelength – Reiterate the importance of choosing the correct wavelength for your skin and hair type to ensure safe and effective treatment.
If you have any additional questions or concerns about choosing the right device or the suitability of laser hair removal for your specific needs, please don't hesitate to reach out to our team.
We are here to provide further guidance and personalized advice to help you make an informed decision.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights into the importance of wavelength specifications in choosing a laser hair removal device.
Remember, informed decisions lead to successful outcomes.
Feel free to reach out to our dermatology clinic for personalized advice and expert guidance on selecting the perfect device for your needs.
Your safety and satisfaction are our top priorities.
References:
- Gençoğlu, Ş. (2023). Efficacy and Safety of Alexandrite and Nd: YAG Laser Combination in Permanent Hair Removal. International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 419-427.
- Gold, M. H., & Goren, H. (2015). The Effect of Novel Low Energy Pulsed Light Combined with Galvanic Energy for Home-Use Hair Removal of Dark Skin. Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 5(4), 283-290.
- AL-Hamamy, H. R., Saleh, A. Z., & Rashed, Z. A. (2015). Evaluation of effectiveness of diode laser system (808 nm) versus Intense Pulse Light (IPL) in the management of unwanted hair: A split face comparative study. International Journal of Medical Physics, Clinical Engineering and Radiation Oncology, 4(01), 41.
- Pall, A., & Viera-Mármol, G. (2022). Triple wavelength and 810 nm diode lasers for hair removal: a clinical and in silico comparative study on Indian skin. Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 12(4), 164-173.
- Gold, M. H., Hellman, J., Dahan, S., & Mulholland, R. S. (2019). Clinical evaluation of a novel blended mode diode laser for hair removal. Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 9(01), 19.
- Russe, E., Purschke, M., Herold, M., Sakamoto, F. H., Wechselberger, G., & Russe‐Wilflingseder, K. (2020). Evaluation of safety and efficacy of laser hair removal with the long‐pulsed 755 nm wavelength laser: a two‐center study with 948 patients. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, 52(1), 77-83.