Pilonidal disease often misconceived and frequently debilitating, remains a prevalent concern among adolescents and young adults. Defined as the occurrence of cysts between the buttocks, this condition stems from an inflammatory reaction to trapped hair or debris within the buttock crease. Studies suggest its incidence lies between 26 to 100 per 100,000 individuals, posing substantial challenges due to its painful and recurrent nature. Moreover, lifestyle factors like a sedentary lifestyle and obesity further compound the risk for this condition.
Despite various treatment approaches, pilonidal disease persists, impacting individuals' daily lives significantly. Patients often grapple with psychological stress, missing school, sports, and social activities due to recurrent bouts of this condition. The standard treatments typically involve hair removal through razors or creams, alongside meticulous cleanliness of the affected area. However, their efficacy in preventing recurrences remains limited.
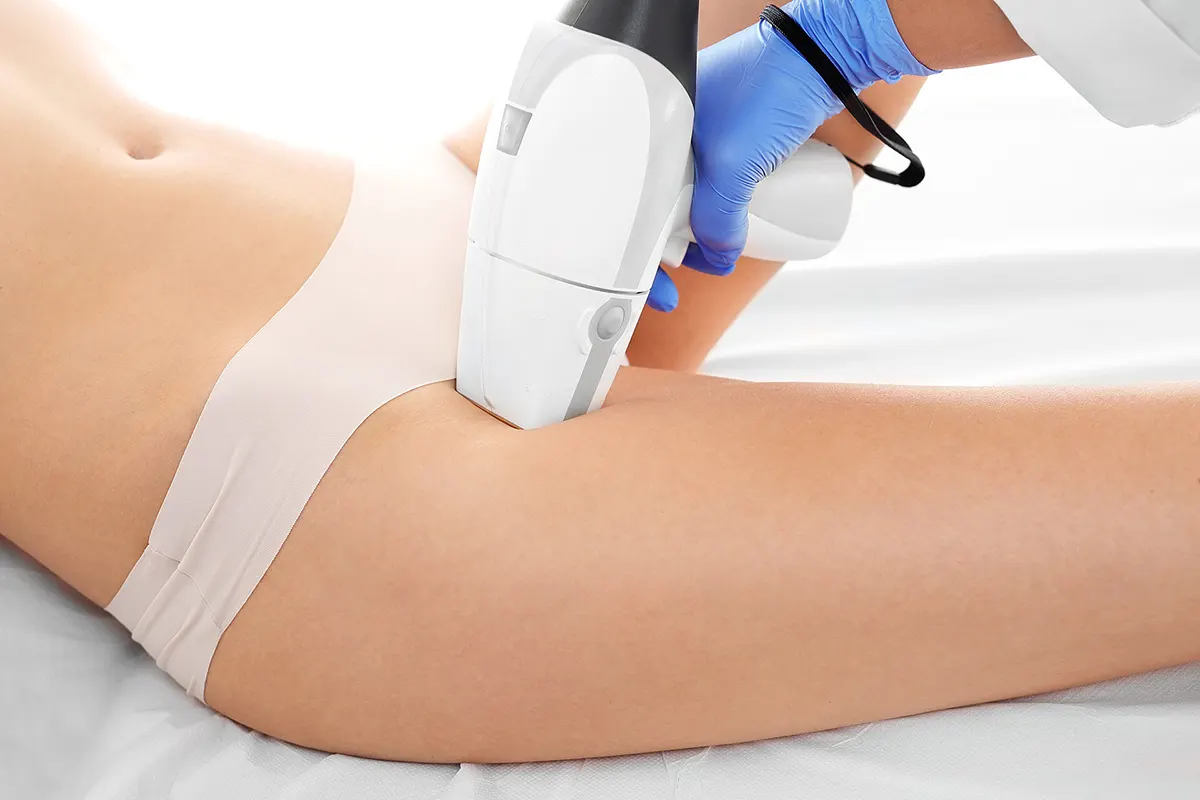
Recent advancements have introduced laser epilation, also known as laser hair removal, as a promising addition to the armamentarium against pilonidal disease. This FDA-approved procedure, administered by trained professionals, offers a more durable and potentially effective means of hair removal. Laser epilation could substantially reduce the risk of recurrence when incorporated into the treatment regimen.
In this comprehensive review, we delve into the depths of pilonidal disease and explore the emergence of laser epilation as a prospective treatment. We analyze the existing research, discuss its efficacy, address practical considerations, and spotlight the challenges and potential future advancements in this domain. By unraveling the facets of laser epilation in pilonidal disease, we aim to understand its impact and implications in clinical practice comprehensively.
Understanding Pilonidal Disease
Causes and Risk Factors
Etiology:
Pilonidal disease, rooted in the intergluteal cleft, is believed to stem from an inflammatory response triggered by hair follicles. When hair or debris infiltrates and accumulates within this region, it fosters the development of cysts or abscesses. Often viewed as a reaction to the hair's presence, the condition manifests as painful, recurrent cysts and sinus tracts.
Risk Factors:
- Lifestyle Factors: Sedentary lifestyles, characterized by prolonged sitting or lack of physical activity, contribute significantly to the development of Pilonidal Disease. Individuals who spend extended periods sitting, especially with inadequate breaks or movements, subject the intergluteal area to continuous pressure and friction. This prolonged pressure exacerbates the likelihood of hair and debris getting trapped in the cleft, fostering an environment conducive to cyst or abscess formation. Additionally, obesity amplifies this risk due to increased adipose tissue in the buttock area, which can further intensify friction and pressure, exacerbating the condition.
- Anatomical Predisposition: Certain anatomical features play a crucial role in predisposing individuals to Pilonidal Disease. A deep intergluteal cleft or excessive hair growth in the area creates an environment where hair and debris are more likely to accumulate. The deeper the cleft, the greater the chance of hair penetration and subsequent inflammation. Excessive hair growth, particularly when coarse or curly, contributes to increased likelihood of hair becoming embedded in the skin, initiating the inflammatory response characteristic of this condition.
- Age and Gender: Pilonidal Disease primarily affects adolescents and young adults, with its onset often occurring between the ages of 15 to 30. Among this demographic, males are notably more prone to developing the condition, with a prevalence almost twice as high as in females. The predisposition in males is partly attributed to hairier skin in the intergluteal area and potentially increased friction due to male clothing styles. Hormonal differences may also play a role, although the exact influence remains subject to further research. However, regardless of gender, the condition often emerges during this stage of life, marked by increased hair growth, prolonged sitting during school or work, and other factors contributing to the development of Pilonidal Disease.
Understanding these risk factors provides critical insights into the multifaceted nature of Pilonidal Disease development. It emphasizes the importance of preventive measures, such as promoting an active lifestyle, maintaining proper hygiene, and considering modifications for individuals with anatomical predispositions, to mitigate the risk and occurrence of this challenging condition.
Impact on Quality of Life
Physical Consequences:
- Pain and Discomfort: Pilonidal Disease is notorious for causing severe pain and discomfort, particularly during flare-ups or infections. Individuals afflicted by this condition often experience intense localized pain in the intergluteal area. This discomfort can range from a mild, persistent ache to sharp, stabbing pains, significantly impacting their ability to perform routine activities such as sitting, walking, or even lying down comfortably. During acute phases, the pain can be debilitating, causing immense distress and affecting daily life and work productivity.
- Recurrences and Infections: The recurrent nature of Pilonidal Disease exacerbates the physical strain on affected individuals. Frequent flare-ups and recurrent infections in the form of abscesses or draining sinus tracts lead to persistent discomfort and distress. The cycle of healing and re-inflammation not only intensifies physical discomfort but also heightens psychological stress due to the unpredictability and repetitive nature of the condition. Individuals often find themselves in a perpetual cycle of discomfort, seeking relief but facing frequent recurrences that compromise their quality of life.
- Impaired Mobility: Severe episodes of Pilonidal Disease can severely restrict an individual's mobility. During acute bouts or following surgical interventions, movement can become severely restricted due to the intense pain or post-operative discomfort. The limitations in mobility not only hinder day-to-day activities but also lead to social withdrawal, as individuals might find it challenging to engage in physical activities, work, or social interactions.
The physical consequences of Pilonidal Disease extend beyond mere discomfort; they profoundly impact an individual's ability to lead a normal life. The recurring nature of the condition, coupled with the pain and discomfort associated with it, disrupts daily routines, impairs mobility, and significantly diminishes the overall quality of life for those affected. Addressing these physical implications is crucial in developing more effective strategies for managing and treating this challenging ailment.
Psychosocial and Emotional Implications:
- Psychological Stress: The recurring nature of Pilonidal Disease takes a considerable toll on the mental well-being of affected individuals. The uncertainty of when the next flare-up might occur, coupled with the pain and discomfort experienced during these episodes, contributes significantly to psychological distress. Anxiety often prevails among patients, manifesting as heightened worry and unease about the condition's persistence and impact on their daily lives. Living with the constant fear of recurrence can lead to increased stress levels, exacerbating emotional strain and impacting overall mental health.
- Impact on Daily Life: The chronic nature of Pilonidal Disease disrupts the daily lives of individuals grappling with the condition. Frequent episodes of discomfort and the need for ongoing medical attention often force patients to miss out on essential aspects of life, such as attending school, work, or social events. These recurrent absences and interruptions in routine activities lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and a sense of being disconnected from regular life experiences. The need for frequent medical attention, including visits to healthcare providers or hospitals, also imposes additional stressors, disrupting normalcy and adding to the emotional burden.
The psychosocial and emotional implications of Pilonidal Disease extend beyond the physical discomfort, significantly impacting the mental well-being and overall quality of life of affected individuals. The persistent anxiety stemming from the unpredictability of the condition, coupled with the limitations it imposes on daily activities and social engagements, underscores the need for comprehensive approaches that address not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional distress experienced by patients.
Current Treatment Methods and Limitations
Conventional Treatments:
- Hair Removal Techniques: Traditional methods such as razor shaving and the application of depilatory creams are frequently utilized to eliminate hair in the affected intergluteal area. These methods aim to reduce the potential for hair to infiltrate and cause inflammation by removing surface hair. However, their effectiveness in preventing recurrences is limited as they only offer temporary relief. Despite efforts to remove surface hair, the underlying issue of hair follicles embedded in the skin remains unresolved, leading to continued susceptibility to recurrent cysts or abscesses.
- Emphasis on Cleanliness: Meticulous cleanliness and maintaining optimal hygiene in the intergluteal cleft are fundamental aspects of managing Pilonidal Disease. Patients are advised to keep the affected area clean, dry, and free from debris to mitigate the risk of infections and recurrences. Regular cleansing routines, such as daily washing and drying, are recommended to prevent the accumulation of hair and other irritants in the affected region. While this emphasis on cleanliness is crucial for minimizing the risk of exacerbating the condition, it primarily focuses on symptomatic relief and does not address the root cause of the disease.
Limitations:
- Recurrence Rates: Despite employing conventional treatments like hair removal techniques and emphasizing cleanliness, the recurrence rates of Pilonidal Disease remain notably high. Studies indicate that approximately one-third of patients experience recurrences within a year post-initial treatment. These conventional methods often provide temporary relief by managing symptoms but fail to address the underlying cause, leading to continued susceptibility to recurrent cysts and sinus tracts.
- Temporary Solutions: Conventional treatments for Pilonidal Disease primarily offer temporary relief rather than permanent resolution. While these methods may alleviate immediate symptoms and provide short-term comfort, they lack the efficacy to prevent recurrences in the long run. The temporary nature of these treatments poses challenges for individuals seeking a more definitive and lasting solution to the persistent issue of recurrent cysts and abscesses.
Understanding the etiology, impact, and current treatment modalities underscores the need for more effective strategies in managing pilonidal disease. This sets the stage for exploring laser epilation as a potential breakthrough in combating the challenges posed by this condition.
Laser Epilation as an Emerging Treatment
Laser Epilation: An Overview
Definition:
Laser epilation, synonymous with laser hair removal, involves using concentrated light energy to eliminate or reduce hair growth in specific areas of the body. This treatment modality aims to reduce or eliminate unwanted hair growth in specific regions of the body, including but not limited to the intergluteal area affected by Pilonidal Disease. By focusing on specific areas, lasers penetrate the skin and target the melanin pigment present in hair follicles without affecting the surrounding skin, leading to the disruption of hair growth cycles.
Evolution of Laser Epilation for Pilonidal Disease
Historical Context:
- Emergence in Dermatology: Initially introduced primarily for cosmetic purposes, laser hair removal quickly gained traction within the field of dermatology due to its precision and effectiveness in addressing unwanted hair growth. The procedure's ability to selectively target hair follicles while minimizing damage to surrounding skin made it a sought-after treatment in the realm of aesthetics.
- Extension to Medical Applications: The transition of laser epilation from a cosmetic procedure to exploring medical applications marked a significant paradigm shift. Beyond its initial cosmetic use, the technology behind laser hair removal started garnering attention for its potential in addressing various medical conditions. The exploration of laser epilation for medical conditions, such as Pilonidal Disease, represents a crucial extension of its application beyond aesthetics. This shift in perspective recognized the procedure's potential for therapeutic purposes beyond cosmetic treatments.
The historical evolution of laser epilation denotes a shift in perception and application, where a technology primarily embraced for cosmetic enhancements found new avenues in addressing medical conditions. This extension of laser epilation into the domain of medical applications, specifically for conditions like Pilonidal Disease, highlights the adaptability and potential versatility of this technology in diverse healthcare settings beyond its initial cosmetic focus.
Development and Adaptation:
- Tailoring for Specific Conditions: Adapting laser epilation specifically for Pilonidal Disease represents a groundbreaking approach in managing this challenging condition. The tailored use of laser technology aims to target hair follicles in the intergluteal area affected by Pilonidal Disease, where embedded hair is a significant contributing factor to the condition's recurrence. By focusing on this specific region, laser epilation endeavors to disrupt hair growth and mitigate the inflammatory response triggered by hair penetration, potentially reducing the likelihood of recurrent cysts or abscesses.
- Research and Trials: Ongoing research initiatives and clinical trials play a pivotal role in assessing the efficacy, safety, and feasibility of laser epilation as a potential treatment avenue for Pilonidal Disease. These endeavors involve systematic evaluation and validation of the procedure's effectiveness in reducing hair growth and preventing recurrence in individuals with this condition. The research and trials seek to establish evidence-based protocols, optimal treatment parameters, and safety guidelines for the application of laser epilation in managing Pilonidal Disease. This systematic approach ensures that the procedure is conducted with precision and safety, considering factors such as patient selection criteria, treatment intervals, and potential adverse effects.
The development and adaptation of laser epilation for Pilonidal Disease underscore a pioneering shift towards addressing the root cause of the condition rather than merely managing its symptoms. Through ongoing research and clinical trials, the aim is to solidify its role as a potential therapeutic intervention, paving the way for more effective and targeted approaches in managing this recurrent and challenging ailment.
Mechanism of Laser Epilation in Treating Pilonidal Disease
Targeting Hair Follicles:
- Selective Absorption: Laser energy emitted during epilation specifically targets the melanin pigment found in hair follicles. This targeted energy absorption heats the follicles, leading to their damage or destruction. By selectively targeting melanin, lasers aim to hinder or reduce future hair growth in the treated area.
- Anagen Hair Response: The effectiveness of laser treatment is notably higher during the anagen phase of hair growth. This phase represents the active growth stage of hair follicles, making them more responsive to treatment. As a result, targeting hair follicles in the anagen phase maximizes the efficacy of laser epilation, providing optimal and longer-lasting results.
Addressing Root Cause:
- Hair Removal in Affected Area: Laser epilation specifically focuses on removing hair from the intergluteal region affected by Pilonidal Disease. By effectively eliminating hair in this area, the procedure aims to address a fundamental contributor to the condition's recurrence. The presence of hair within the intergluteal cleft can lead to penetration, triggering an inflammatory response and the formation of recurrent cysts or sinus tracts.
- Preventing Recurrence: The primary objective of laser epilation in Pilonidal Disease management is to eliminate existing hair and impede its regrowth in the affected area. By disrupting hair growth cycles, the procedure endeavors to lower the chances of recurrent cysts and sinus tract formation. This preventive approach aims to reduce the inflammatory response triggered by hair penetration, potentially decreasing the frequency and severity of recurring episodes associated with the condition.
The mechanism of Laser Epilation in treating Pilonidal Disease primarily revolves around targeting hair follicles within the intergluteal area. Through selective absorption of laser energy and the removal or reduction of hair growth, the procedure aims to address the root cause by hindering hair penetration and, consequently, lowering the risk of recurrent cysts and sinus tracts formation, potentially offering relief and reducing the burden of this chronic condition.
Clinical Application in Pilonidal Disease
Treatment Protocol:
- Post-Surgical Intervention: Laser hair removal as an adjunct to surgical excision represents an innovative therapeutic strategy in managing Pilonidal Disease. Following surgical intervention to address existing cysts or sinus tracts, laser epilation is integrated into the treatment plan. The aim is to complement surgical excision by targeting remaining or regrowing hair follicles in the intergluteal region, reducing the likelihood of recurrence.
- Laser Parameters: Specific laser wavelengths and parameters are meticulously tailored for treating Pilonidal Disease. These parameters are optimized to ensure both efficacy and safety during laser epilation. Precision in selecting appropriate wavelengths and parameters enhances the procedure's effectiveness in selectively targeting hair follicles while minimizing adverse effects on surrounding tissues.
Potential Benefits:
- Reduced Recurrence Rates: Initial studies investigating the incorporation of laser epilation post-surgery have shown promising results in reducing recurrence rates of Pilonidal Disease. The combination of surgical excision followed by laser hair removal aims to effectively eliminate hair in the treated area, potentially decreasing the likelihood of hair penetration and subsequent cyst or sinus tract formation.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: The integration of laser epilation into the treatment regimen post-surgery may contribute to improved patient outcomes. By potentially lowering recurrence rates, this adjunctive therapy seeks to enhance patient quality of life by reducing discomfort associated with recurrent episodes. Moreover, decreasing the frequency and severity of recurrences could alleviate the psychosocial stress and anxiety often experienced by individuals grappling with the chronic nature of Pilonidal Disease.
The clinical application of laser epilation as part of a comprehensive treatment protocol for Pilonidal Disease involves post-surgical intervention aimed at reducing the risk of recurrence. By customizing laser parameters and employing this adjunctive therapy post-surgery, the goal is to potentially improve patient outcomes, minimize recurrence rates, and alleviate the physical and emotional burden of this challenging condition.
Research and Studies
Research and Studies:
Scientific Inquiry Supporting Laser Epilation
Key Studies:
- Clinical Trials: Noteworthy research spearheaded by Dr. Peter C. Minneci, Chair of Surgery at Nemours Children's Health, Delaware Valley, has highlighted the efficacy of laser epilation in mitigating recurrence rates of Pilonidal Disease. Dr. Minneci's research endeavors underscore the potential benefits of incorporating laser hair removal into the treatment paradigm for this condition.
Dr. Peter C. Minneci's clinical trials and research efforts contribute significantly to understanding the role of laser epilation in reducing recurrence rates of Pilonidal Disease. These studies serve as a pivotal reference point, providing evidence-based insights into the effectiveness and potential impact of laser hair removal as an adjunctive therapy in managing this condition.
The research conducted by Dr. Peter C. Minneci and studies involving sizable patient cohorts play a crucial role in clinically validating the efficacy and potential role of laser epilation in the management of Pilonidal Disease. These findings contribute to establishing evidence-based guidelines and treatment protocols for healthcare practitioners. - Enrollment and Observations: Studies involving cohorts of patients, such as the one with 302 participants enrolled at Nationwide Children's Hospital, have provided substantial data regarding the advantages and effectiveness of laser epilation in managing Pilonidal Disease. These observations offer valuable insights into the outcomes and benefits of this treatment modality within a diverse patient population.
Research involving substantial cohorts of patients, like the study at Nationwide Children's Hospital, offer comprehensive data points and real-world observations regarding the benefits and outcomes of laser epilation. These studies not only contribute to the body of evidence supporting this treatment approach but also provide insights into the treatment's feasibility and efficacy across a diverse patient demographic.
The outcomes and insights from these studies hold the potential to garner wider recognition within the medical community, potentially leading to the adoption of laser epilation as a recognized adjunctive therapy in the multifaceted management of Pilonidal Disease. This recognition may influence clinical practice, promoting the integration of laser hair removal into treatment protocols.
Reduction in Recurrence Rates: Insights from Results
Comparative Analysis:
- Laser Epilation Plus Standard Treatment vs. Standard Treatment Alone: Comparative analyses between cohorts receiving laser epilation alongside standard treatment and those solely undergoing standard therapeutic approaches reveal a significant contrast in recurrence rates. The cohort receiving the combined therapy of laser epilation and standard treatment demonstrates notable differences in recurrence rates compared to those undergoing standard treatment alone.
- Statistics and Figures: Detailed statistical breakdowns elucidate the tangible reduction in recurrence percentages observed in patients undergoing laser epilation in conjunction with standard treatment protocols. These statistical analyses present compelling evidence showcasing the potential of laser epilation in minimizing the recurrence of Pilonidal Disease episodes.
Implications of Findings:
- Efficacy of Combined Therapy: The comparative analysis demonstrating a significant contrast in recurrence rates between cohorts suggests the efficacy of combining laser epilation with standard treatment protocols. These findings indicate that integrating laser hair removal into the treatment regimen may contribute to reducing the frequency of recurrent Pilonidal Disease episodes.
- Clinical Significance: The statistical breakdowns substantiating the reduction in recurrence percentages underscore the clinical significance of incorporating laser epilation as an adjunctive therapy. The observed reduction in recurrence rates signifies the potential of laser hair removal in enhancing the effectiveness of standard treatment approaches, potentially offering improved outcomes for individuals affected by Pilonidal Disease.
These comparative analyses and statistical breakdowns highlight the promising potential of laser epilation as an adjunctive therapy in minimizing the recurrence rates of Pilonidal Disease. The findings suggest that integrating laser hair removal with standard treatment approaches may lead to more favorable outcomes, potentially reducing the burden of recurrent episodes associated with this chronic condition.
Patient Outcomes and Satisfaction: A Comprehensive Discourse
Impact on Quality of Life:
- Psychosocial and Physical Implications: Post-laser epilation, an in-depth evaluation of patient experiences reveals notable improvements in both physical discomfort and psychosocial stress associated with recurrent Pilonidal Disease episodes. Patients report experiencing reduced pain, discomfort, and distress, indicating a tangible enhancement in their physical well-being following the treatment.
- Resonating Patient Satisfaction: Testimonials and feedback from individuals who have undergone laser epilation highlight heightened satisfaction levels and perceived benefits when compared to conventional treatments. Patients express increased contentment and relief post-treatment, emphasizing the effectiveness of laser epilation in addressing their condition.
Implications of Patient Satisfaction:
- Improvements in Well-being: The reported improvements in physical discomfort and psychosocial stress post-laser epilation signify a positive impact on patients' overall well-being. By alleviating physical symptoms and reducing the emotional burden associated with recurrent Pilonidal Disease, laser epilation appears to enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
- Preference for Laser Epilation: The resonance of patient satisfaction, highlighted through testimonials and feedback, underscores a preference for laser epilation over conventional treatments. The perceived benefits and heightened satisfaction levels among patients indicate a shift towards considering laser hair removal as a more favorable and effective treatment option for managing Pilonidal Disease.
The comprehensive evaluation of patient outcomes and satisfaction post-laser epilation reveals a significant improvement in both physical discomfort and psychosocial stress associated with recurrent Pilonidal Disease. The resonance of heightened patient satisfaction and the perceived benefits when compared to conventional treatments indicate the potential for laser epilation to not only alleviate physical symptoms but also positively impact the overall well-being and satisfaction of individuals grappling with this challenging condition.
Discussion on Clinical Implications
Paving the Way for New Treatment Modalities:
- Implications for Medical Practice: The amalgamation of diverse studies advocating for laser epilation in Pilonidal Disease management positions it as a transformative adjunct treatment modality. The accumulation of empirical evidence from various research endeavors provides a robust foundation for considering laser hair removal as an integral part of the treatment armamentarium.
- Alleviating Patient Burden: The discernible reduction in recurrence rates observed in studies employing laser epilation and the subsequent alleviation of patient distress signify a paradigm shift in patient care. By mitigating the frequency and severity of recurrent episodes, laser epilation holds the potential to redefine patient care paradigms, offering a more effective and patient-centric approach to managing Pilonidal Disease.
Significance of Collective Insights:
- Transformative Impact on Recurrence Rates and Patient Satisfaction: The collective insights gleaned from diverse research studies highlight the transformative impact of laser epilation in mitigating recurrence rates and enhancing patient satisfaction. The observed reduction in recurrence rates, coupled with heightened patient satisfaction levels, underscores the potential of laser hair removal as a pivotal component in managing this challenging medical condition.
- Charting a New Course in Therapeutic Approaches: These findings signify a significant shift in therapeutic approaches for Pilonidal Disease. Emphasizing the pivotal role of laser epilation as an integral component in the multifaceted management of this condition, these insights chart a new course in therapeutic strategies, advocating for the incorporation of laser hair removal into standard treatment protocols.
The culmination of diverse studies and empirical evidence advocating for laser epilation underscores its transformative potential as an adjunctive treatment modality in Pilonidal Disease management. These findings not only emphasize its effectiveness in mitigating recurrence rates but also highlight its role in enhancing patient satisfaction and redefining patient care paradigms, paving the way for a more comprehensive and efficacious approach to managing this challenging medical condition.
Practical Considerations and Implementation
Practical Implementation of Laser Epilation: Accessibility and Affordability
Availability and Accessibility
- Clinical Settings vs. Hair Removal Salons: The current landscape of laser epilation availability is varied, encompassing both medical settings and hair removal salons. While medical settings typically offer a supervised and clinically controlled environment, ensuring adherence to safety protocols, hair removal salons may focus more on cosmetic procedures, potentially lacking the expertise and stringent medical oversight required for medical conditions like Pilonidal Disease.
- Professional Expertise: Practitioners authorized to administer laser epilation in medical settings often include dermatologists, plastic surgeons, or trained medical professionals specializing in laser therapies. They undergo specialized training and certification to perform laser hair removal, ensuring proficiency in the procedure's safe and effective execution.
Financial Considerations: Costs and Comparisons
- Treatment Expenses: Costs associated with laser epilation for Pilonidal Disease may vary based on several factors, including the treatment area's size, the number of sessions required, and the healthcare provider's expertise. A detailed breakdown of costs should encompass consultation fees, session charges, and potential additional expenses related to follow-up appointments or maintenance treatments.
- Comparison with Conventional Treatments: Comparative analysis between the costs of laser epilation and traditional treatments like razor-based or cream-based hair removal methods is essential. While laser epilation may involve higher upfront costs, its potential long-term effectiveness in reducing recurrence rates could potentially outweigh the ongoing expenses associated with conventional, yet less durable, treatments.
Related: Laser Hair Removal Cost & Prices (National Statistics Report)
Patient Decision-making: Weighing Options
- Factors Influencing Choice: Patient decisions regarding treatment for Pilonidal Disease are influenced by various factors. These encompass financial concerns, where patients weigh the upfront costs of laser epilation against potential long-term benefits, efficacy expectations based on treatment effectiveness, and convenience factors such as the number of sessions required and the recovery period.
- Insurance Coverage and Future Prospects: Addressing the current status of insurance coverage for laser epilation is crucial. If insurers cover this treatment modality, it could significantly impact its widespread adoption, making it more accessible to eligible patients. Discussing potential future prospects regarding insurance coverage may shed light on the evolving landscape and potential advancements in financial accessibility.
The practical implementation of laser epilation for Pilonidal Disease involves navigating accessibility, professional expertise, financial considerations, and patient decision-making factors. Evaluating the availability in clinical settings versus hair removal salons, understanding the expertise required, analyzing treatment expenses, and considering insurance coverage are pivotal in empowering patients to make informed decisions regarding their treatment options.
Real-world Application and Comparative Analysis
Efficacy vs. Costs: Weighing the Balance
- Efficacy Metrics: Assessing the efficacy of laser epilation involves evaluating its ability to reduce recurrence rates and improve patient outcomes compared to conventional treatments. Key metrics include recurrence percentages post-treatment, patient-reported improvements in quality of life, and long-term effectiveness in preventing Pilonidal Disease episodes.
- Patient Preferences: Understanding patient preferences is crucial in determining the acceptance and adoption of laser epilation. Factors influencing preferences include treatment effectiveness, comfort during sessions, recovery duration, and the perceived value of long-term benefits versus initial costs.
Healthcare Equity and Access
- Implications for Equitable Care: Exploring the role of insurance coverage or subsidized costs in enhancing healthcare equity can significantly impact laser epilation's accessibility. Discussing potential strategies to ensure widespread access for all eligible patients, regardless of financial constraints, is crucial in promoting equitable healthcare.
- Impact on Patient Experience: Affordability and accessibility are pivotal in shaping patient experiences and adherence to treatment regimens. Increased affordability can positively influence patient experiences by reducing financial barriers, enhancing treatment adherence, and potentially improving overall health outcomes.
A comprehensive assessment encompassing availability, financial implications, and comparisons with conventional treatments empowers both patients and healthcare providers. This evaluation aids in making informed decisions regarding the most suitable therapeutic approach for managing Pilonidal Disease. By considering factors like efficacy, costs, patient preferences, healthcare equity, and access, stakeholders can collaboratively navigate the practical aspects of implementing laser epilation as a viable treatment option.
This comprehensive assessment provides a holistic view of the practical considerations surrounding laser epilation. It focuses on balancing efficacy against costs, understanding patient preferences, advocating for equitable healthcare access, and recognizing the influence of affordability and accessibility on patient experiences. Such insights can guide stakeholders in optimizing therapeutic approaches for Pilonidal Disease management, ensuring both effectiveness and inclusivity in patient care.
Addressing Challenges and Future Prospects
Overcoming Barriers to Adoption: Challenges and Solutions
Insurance Coverage and Access Challenges
- Current Hurdles: Barriers hindering widespread insurance coverage for laser epilation encompass concerns related to costs and the perceived efficacy of the treatment by insurers. Insurers may not yet recognize laser epilation as a standard or sufficiently proven treatment option, leading to reluctance in providing coverage
- Strategies for Expansion: Addressing these challenges could involve collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, insurers, and policymakers. This collaboration aims to generate robust data demonstrating the treatment's effectiveness, fostering discussions to establish standard protocols, and advocating for policy changes that recognize laser epilation as a viable therapeutic option.
Ongoing Research and Future Landscape
- Emerging Research Avenues: Recent studies exploring advancements in laser epilation techniques emphasize developments in novel technologies or procedural enhancements. These may include advancements in laser technology aiming for increased precision, reduced session times, or enhanced safety profiles, potentially making the treatment more efficient and safer for patient
- Unresolved Questions: Persistent gaps in knowledge or areas requiring further investigation include long-term outcomes of laser epilation, optimal treatment protocols, and understanding its effects on different patient demographics. Addressing these gaps can refine treatment approaches and broaden the scope of laser epilation's applicability.
Advancements and Evolution in Laser Epilation
Technological Enhancements and Refinements
- Future Technological Frontiers: Future technological frontiers in laser epilation may include innovations focusing on improved precision, reduced discomfort or side effects, and enhanced safety profiles. These advancements aim to make the treatment more patient-friendly while maintaining its efficacy.
- Patient-Centric Innovations: Innovations targeting enhanced patient comfort during laser treatments, such as advanced cooling systems or pain mitigation techniques, seek to minimize discomfort or side effects, further improving the patient experience.
Holistic Improvement in Patient Care
- Integration with Multidisciplinary Care: The potential integration of laser epilation within a broader spectrum of care involves combining it with complementary treatments or strategies. This integration aims to provide a holistic approach, addressing not only the physical symptoms but also incorporating psycho-social support and personalized treatment plans.
- Patient-Centric Care Models: Proposing holistic care models centered around patient well-being emphasizes the integration of psycho-social support and tailored treatment plans. Such models aim to provide comprehensive care, ensuring patients receive not just treatment but also support that meets their individual needs.
Addressing challenges related to insurance coverage, exploring ongoing research, and advancements in laser technology, alongside proposing patient-centric care models, presents a multifaceted approach. This approach aims to enhance the recognition and utilization of laser epilation, ensuring its efficacy, safety, and inclusivity in Pilonidal Disease management.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive exploration of laser epilation as a revolutionary approach to treating pilonidal disease, we've traversed through the landscape of this emerging therapy. From understanding the disease's burdens to examining laser epilation's transformative potential, this discourse encapsulates a vital paradigm shift in managing this challenging condition.
Recapitulation of Key Insights
- Understanding Pilonidal Disease: An in-depth exploration into the intricate nature of pilonidal disease, shedding light on its origins, its profound impact on patients' lives, and critically examining the limitations inherent in conventional treatment approaches.
- Laser Epilation Unveiled: Unveiling the historical evolution of laser epilation, elucidating its mechanism of action, and highlighting its pivotal role as a beacon of hope in mitigating the recurrence of pilonidal disease.
- Research and Efficacy: A comprehensive review of pivotal studies that presented compelling evidence showcasing the significant reduction in recurrence rates post-laser epilation treatment, thereby substantially enhancing the overall well-being of patients grappling with pilonidal disease.
- Practical Considerations: Delving into the practical aspects encompassing accessibility, costs, and comparisons vis-à-vis traditional treatments, thereby shedding light on the considerable potential and advantages offered by laser epilation in the management of pilonidal disease.
Paving the Path Forward
- Overcoming Challenges: Navigating through obstacles obstructing widespread adoption, particularly in securing comprehensive insurance coverage, involved the presentation of strategic approaches aimed at surmounting these barriers. These strategies focused on advocating for policy changes and generating robust data to demonstrate the efficacy and long-term benefits of laser epilation as a viable treatment option.
- Future Prospects: A forward-looking gaze into the future shed light on ongoing research trajectories, potential technological refinements, and the emergence of holistic patient-centered care models. This outlook emphasizes advancements in laser technology, envisaging enhancements that focus on precision, safety, and increased patient comfort. Moreover, it envisions the integration of laser epilation within a broader spectrum of care, emphasizing personalized treatment plans and a supportive patient-centric approach.
Recommendations and the Path Ahead
Laser epilation's emergence as a beacon of hope in the landscape of pilonidal disease treatment is undeniable. Concerted efforts are imperative to pave the way for its broader integration into clinical practice. Collaboration among stakeholders, continued research endeavors, advocating for insurance coverage, and fostering patient-centric care models are pivotal to unleashing laser epilation's full potential.
As the journey continues towards refining this transformative therapy, it's not merely about eradicating hair; it's about eliminating the impediments to a better quality of life for those grappling with pilonidal disease. Embracing laser epilation is not just about innovation; it's about extending hope to those seeking respite from this debilitating condition.
References:
- Landa, N., Aller, O., Landa-Gundin, N., Torrontegui, J., & Azpiazu, J. L. (2005). Successful treatment of recurrent pilonidal sinus with laser epilation. Dermatologic surgery, 31(6), 726-728.
- Lukish, J. R., Kindelan, T., Marmon, L. M., Pennington, M., & Norwood, C. (2009). Laser epilation is a safe and effective therapy for teenagers with pilonidal disease. Journal of pediatric surgery, 44(1), 282-285.
- Schulze, S. M., Patel, N., Hertzog, D., & Fares, L. G. (2006). Treatment of pilonidal disease with laser epilation. The American surgeon, 72(6), 534-537.
- Halleran, D. R., Onwuka, A. J., Lawrence, A. E., Fischer, B. C., Deans, K. J., & Minneci, P. C. (2018). Laser hair depilation in the treatment of pilonidal disease: a systematic review. Surgical infections, 19(6), 566-572.
- Grabowski, J., Oyetunji, T. A., Goldin, A. B., Baird, R., Gosain, A., Lal, D. R., … & Jancelewicz, T. (2019). The management of pilonidal disease: a systematic review. Journal of pediatric surgery, 54(11), 2210-2221.